Hearing loss can significantly impact communication, social interactions, and overall well-being. For many, acquiring a hearing aid is a crucial step toward improving their quality of life. However, the associated costs can feel overwhelming. This guide explores the factors influencing hearing aid costs, financial assistance options, and practical tips for making an informed decision when investing in your hearing health.
Breaking Down the Costs of Hearing Aids
The price of hearing aids varies widely due to several factors. Understanding these elements can help you plan effectively and make the best choice for your needs.
Types of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in various styles, each with unique features and price ranges:
-
Behind-the-Ear (BTE): Sits behind the ear and connects to an earmold.
Average cost: $1,500–$3,000 each. -
In-the-Ear (ITE): Custom-fit for the outer ear.
Average cost: $1,500–$3,500 each. -
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC): Discreet design with the receiver in the ear canal.
Average cost: $1,000–$3,000 each. -
Completely-in-Canal (CIC): Fits entirely inside the ear canal.
Average cost: $2,000–$4,000 each.
Advanced Features and Technology
Modern hearing aids offer features like Bluetooth connectivity, noise cancellation, and digital sound processing to enhance the user experience. These technologies, while valuable, can push costs to $1,000–$6,000 per device.
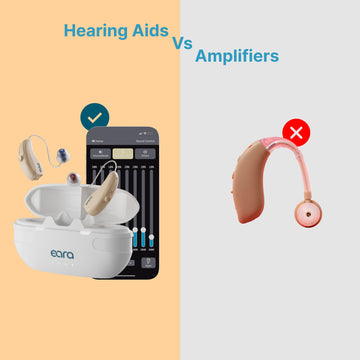
However, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids like the Explore Li+ offer the same advanced features—including Bluetooth connectivity, noise cancellation, and personalized programming—at a fraction of the cost. By eliminating the need for expensive fittings and appointments, OTC hearing aids provide an affordable and high-quality alternative for hearing support.
Financial Assistance for Hearing Aids
Given the costs, exploring financial assistance options can make hearing aids more accessible:
Insurance Coverage
- Health Insurance: Some plans offer partial coverage or discounts.
- FSAs and HSAs: Use pre-tax dollars to reduce out-of-pocket expenses.
Government Programs
- Medicaid: Coverage varies by state, so check local eligibility.
- Medicare: May cover hearing-related evaluations in specific cases.
- Veterans Affairs (VA): Veterans with service-related hearing loss may qualify for free or discounted hearing aids.
Non-Profit Organizations
Groups like the Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA) and local charities may offer grants or reduced-cost devices.
The Rise of OTC Hearing Aids
OTC hearing aids have revolutionized hearing care by offering:
- Affordability: Priced between $200 and $1,000, they are accessible to more users.
- Convenience: Self-fitting options allow users to adjust settings with smartphone apps.
- Availability: Widely available online and in stores, they eliminate the need for prescriptions.
The Explore Li+ OTC Hearing Aids exemplify this innovation. With features like Bluetooth connectivity, rechargeable batteries, and customizable sound profiles, they provide the performance of traditional hearing aids at a fraction of the cost.
Explore Li+: Affordable, High-Quality OTC Hearing Aids
Explore Li+ Self-Fitting Bluetooth OTC Hearing Aids by Eara Hearing offer a revolutionary approach to better hearing. These self-fitting, Bluetooth-enabled OTC hearing aids combine cutting-edge technology with an accessible price point, providing a practical solution for individuals seeking high-quality hearing support.
Features of Explore Li+
-
Advanced Noise Cancellation:
Filters out background noise for clearer conversations. -
Bluetooth Connectivity:
Stream music, calls, and media directly from your devices. -
Rechargeable Convenience:
Long-lasting battery life with fast recharging. -
Customizable Settings:
Tailor your hearing experience with an easy-to-use app. -
Affordable Pricing:
High-end features at a fraction of traditional hearing aid costs.
Eara Hearing: Expert Guidance
Navigating the world of hearing aids can feel overwhelming, but Eara Hearing is here to help. Our 24/7 customer service and free audiologist consultations ensure you have access to expert support whenever you need it.
Whether you’re adjusting to your new devices, troubleshooting, or optimizing your settings, our professionals are dedicated to empowering you with the tools and knowledge for better hearing.
Unlocking the Path to Better Hearing
Investing in hearing aids is a step toward transforming your life. By understanding the costs, exploring financial options, and considering innovative solutions like OTC hearing aids, you can find the right support for your needs. Remember, your hearing health is invaluable, and taking action today can lead to a brighter, more engaged tomorrow.